I think that it is a necessary first step to outline the scope of what Sustainability entails. Before I begin this first rough cut exploration, let me reiterate the context of this post i.e. the first blog carnival of 2008 hosted at Sourcing Innovation by Michael Lamoureux. To that end, I reiterate my solicitation from you my readers toward contributions, comments, disagreement (mild or vehement), skepticism et al.
So, what is Sustainability? In some sense, Sustainability is a superset of a Sustainable Development, which is the most common route of foundational definition that I have come across so far. Even so, different individuals and committees (on account of their professions, persuasions etc) define it in different ways but here’s a first stab at it:
"Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs."
This definition of Sustainable development owes its elucidation to the Brundtland Report (Brundtland Commission, formally the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED), known by the name of its Chair Gro Harlem Brundtland, convened by the United Nations in 1983).
Here is a graphic that succinctly describes the UN’s hopes concerning sustainable development. I used the word "hopes" quite deliberately because that is the reality of it.
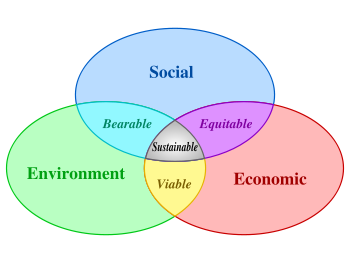
But do take heed,
Sustainable Development is an ambiguous concept, as a wide array of views fall under its umbrella. The concept has included notions of weak sustainability, strong sustainability and deep ecology. Different conceptions also reveal a strong tension between ecocentrism and anthropocentrism. Thus, the concept remains weakly defined and contains a large amount of debate as to its precise definition.
During the last ten years, different organizations have tried to measure and monitor the proximity to what they consider sustainability by implementing what has been called sustainability metric and indices.
Nevertheless, such a concept – Sustainable Development would be a cause dead on arrival if there were no metrics/indices to track where the world at large is with respect to it. And exceeding one’s expectation, there are a host of them – some of them being (summarized from Sustainability metric and indices):
1. The "Daly Rules" – suggested are the following three operational rules (or more like guidelines)
- Renewable resources such as fish, soil, and groundwater must be used no faster than the rate at which they regenerate.
- Nonrenewable resources such as minerals and fossil fuels must be used no faster than renewable substitutes for them can be put into place.
- Pollution and wastes must be emitted no faster than natural systems can absorb them, recycle them, or render them harmless.
2. The Natural Step/System Conditions of Sustainability – Within this framework, In a sustainable society, nature is not subject to systematically increasing:
- concentrations of substances extracted from the Earth’s crust;
- concentrations of substances produced by society;
- degradation by physical means and, in that society. . .
- people are not subject to conditions that systematically undermine their capacity to meet their needs.
3. Life Cycle Assessment – The resultant is a composite measure of sustainability.
It analyses the environmental performance of products and services through all phases of their life cycle: extracting and processing raw materials; manufacturing, transportation and distribution; use, re-use,maintenance; recycling, and final disposal.
4. Energy, Emergy and Sustainability Index (SI) – Emergy (Embodied energy) is defined as,
the quantity of energy required to manufacture, and supply to the point of use, a product, material or service.
Emergy Yield Ratio is Emergy of an output divided by Emergy of all inputs and Environmental Loading Ratio is purchased and nonrenewable indigenous emergy to free (or renewable) environmental emergy.
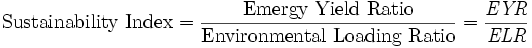
5. The World Business Council for Sustainable Development approach – Lastly, since everyone has so far been talking about how to let businesses run, how long would it be before businesses themselves got into the act.
- Throughout the economy there are widespread untapped potential resource productivity improvements to be made to be coupled with effective design.
- There has been a significant shift in understanding over the last three decades of what creates lasting competitiveness of a firm.
- There is now a critical mass of enabling technologies in eco-innovations that make integrated approaches to sustainable development economically viable.
- Since many of the costs of what economists call
